以下のライブラリを CocoaPods で管理していたが、Swift Package Manager(Xcode)管理に移行してみる。
- SwiftLint
- LicensePlist
- Firebase
- AnalyticsWithoutAdIdSupport
- Crashlytics
以下が、その手順。
CocoaPods でのライブラリ管理を削除
まず CocoaPods でのライブラリ管理をやめる。
以下を実行して、*.pbxproj から Pods_XXX.framework への参照と Pods フォルダを削除する。
pod deintegrate
上記コマンドでは消えない CocoaPods 関連のファイルを、手動で削除する。
- *.xcworkspace
- Podfile
- Podfile.lock
※必要に応じて .gitignore からも CocoaPods 関連ファイルの記述を削除する(たとえば、 Pods フォルダとか)
Xcode で *.xcodeproj を開く。
Xcode 左側の Project Navigator に Pods フォルダの参照が残っている場合は、削除する。
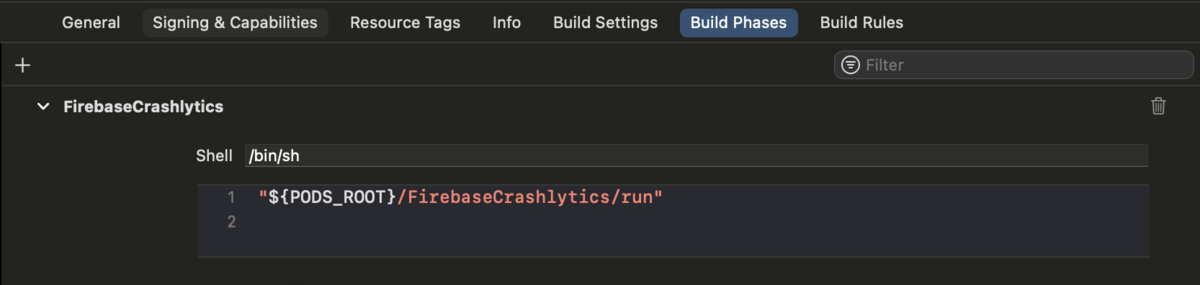
BuildPhase にある Pods を利用した SwiftLint, LisencePlist, Crashlytics のスクリプトを削除する。


Swift Package Manager でライブラリを追加
Package dependencies から + ボタンをクリックしてライブラリを追加する。
SwiftLint
公式ドキュメントのこのあたりが参考になる。
パッケージ追加の画面で以下を検索して、Add Package する。
https://github.com/realm/SwiftLint
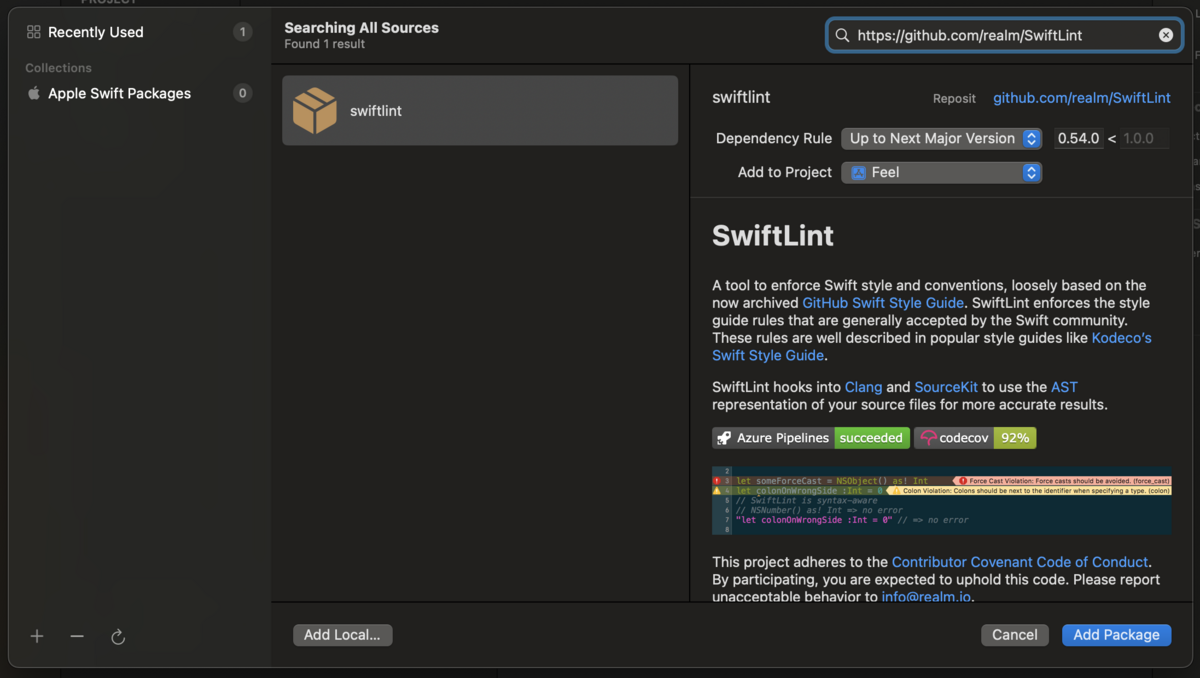
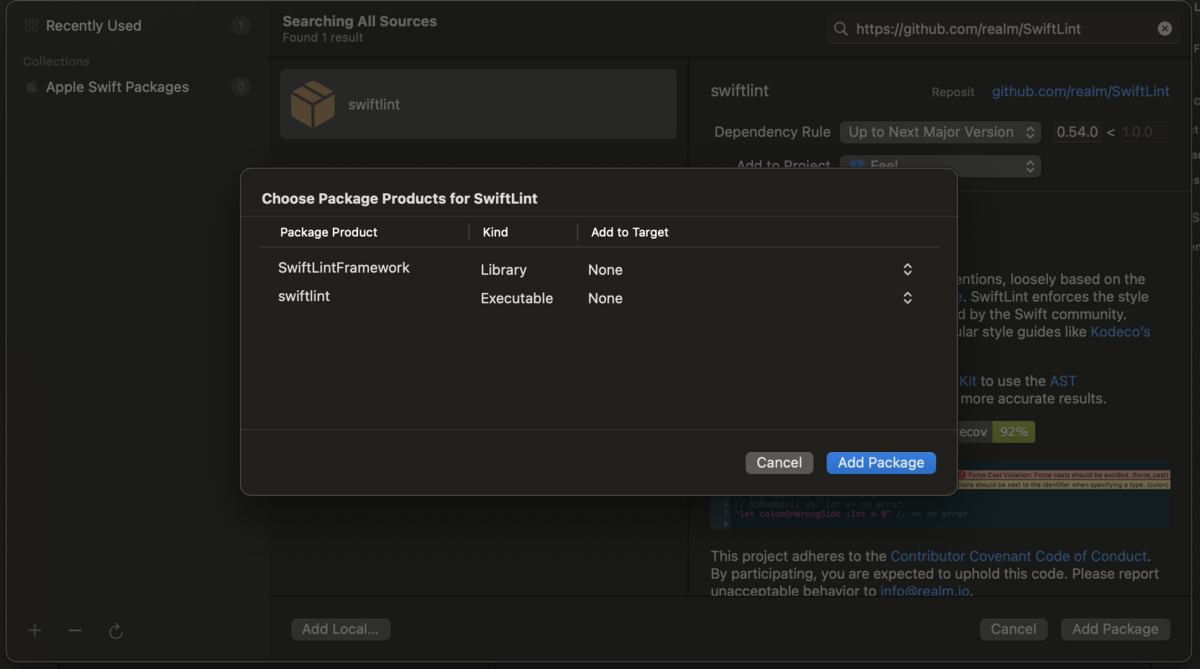
Package Product をターゲット追加する画面が表示されるので、すべて「None」を選び、ターゲット追加しない。Add Package を押す。
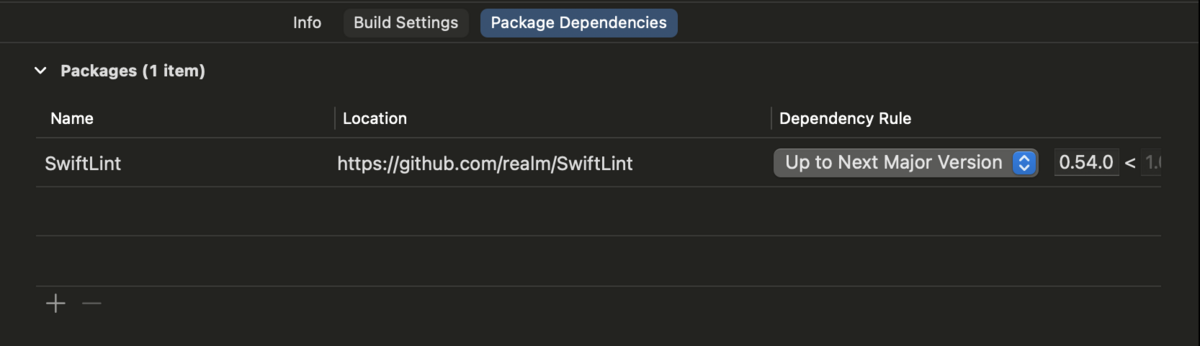
Xcode プロジェクトに Package が追加されたことが確認できる。
次に、Lint が実行されるように、Build Tool Plug-ins を設定する。
Lint 対象のターゲットを選び、Build Phases から Run Build Tool Plug-ins の項目を開き、+ボタンを押す。
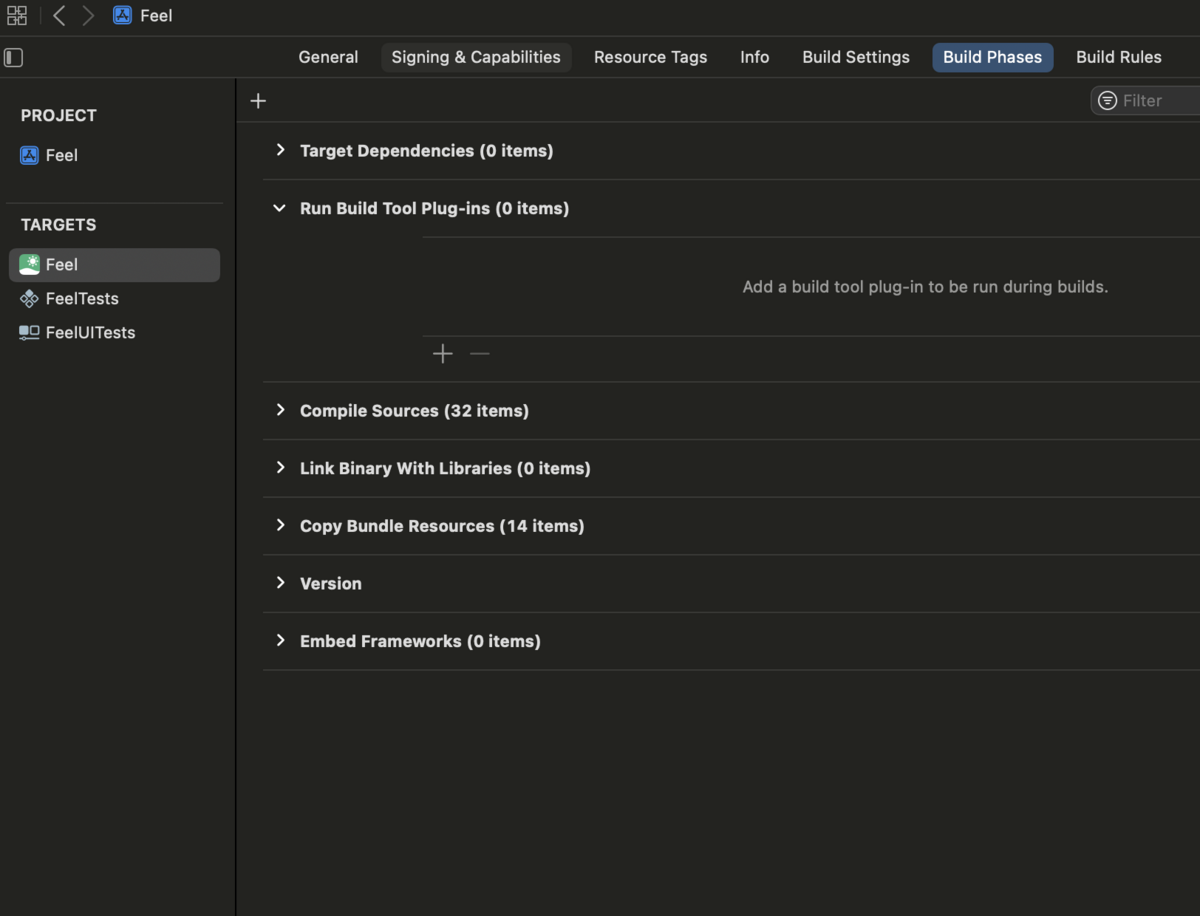
SwiftLintPlugin を選び、Add する。

SwiftLintPlugin が追加されたことが確認できる。
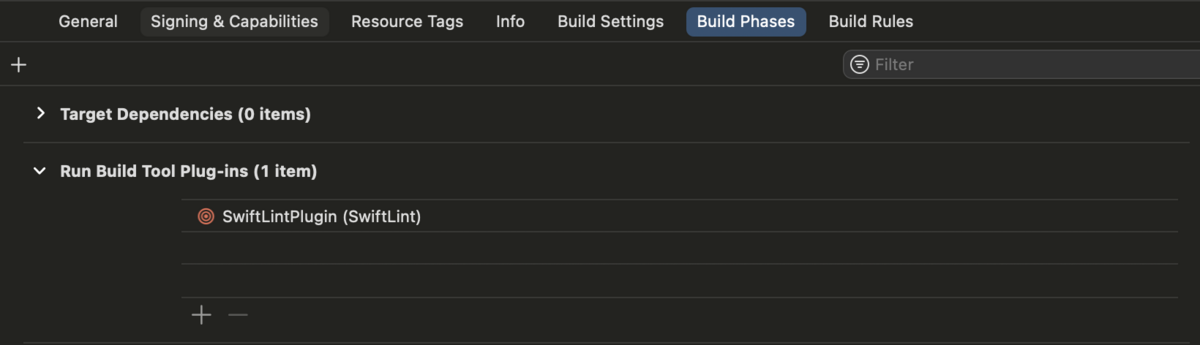
この状態で、ビルドすると SwiftLint が実行される。
プロジェクトのルートフォルダに .swiftlint.yml がある場合は、そこから Lint の設定が読み込まれる。
LicensePlist
公式ドキュメントのこのあたりが参考になる。
パッケージ追加の画面で以下を検索して、Add Package する。
https://github.com/mono0926/LicensePlist
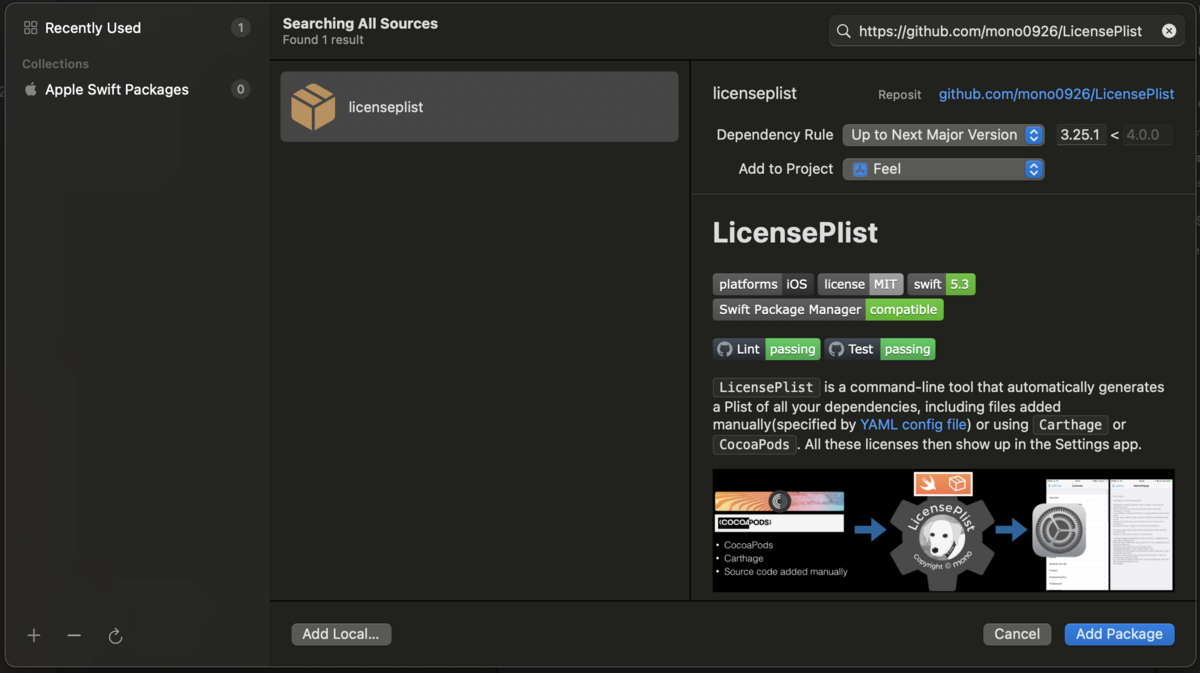
Package Product をターゲット追加する画面が表示されるので、すべて「None」を選び、ターゲット追加しない。Add Package を押す。
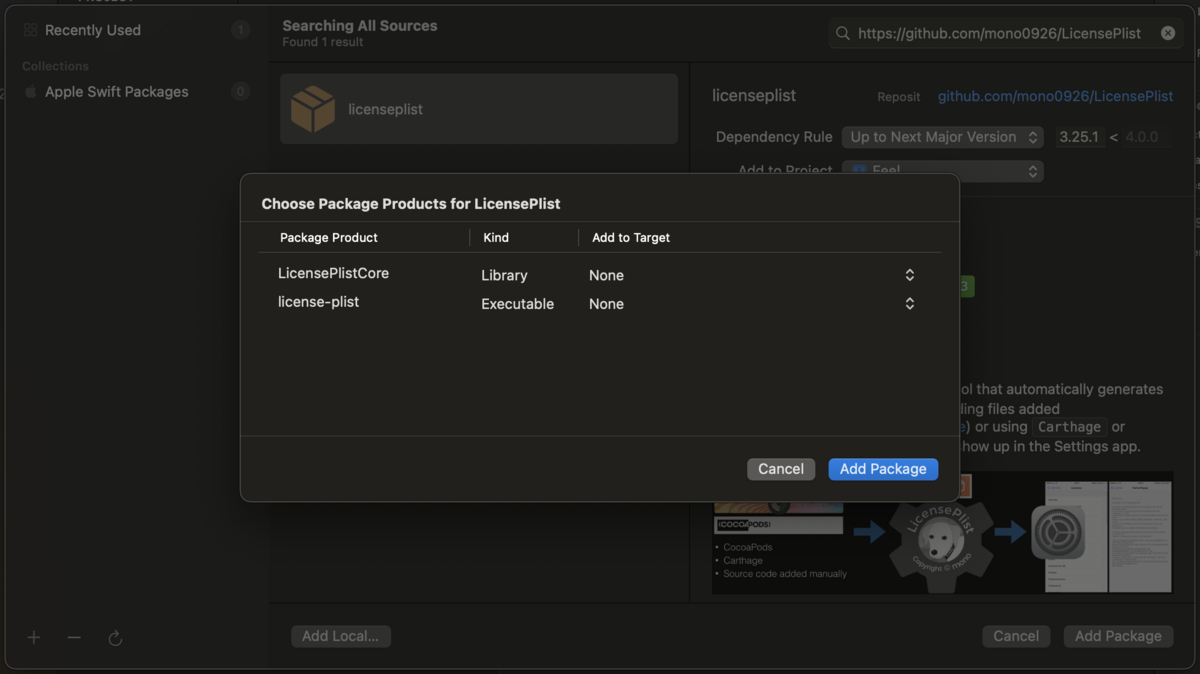
Xcode プロジェクトに Package が追加されたことが確認できる。

LicensePlist のファイルが生成されるように、Build Tool Plug-ins を設定する。
対象のターゲットを選び、Build Phases から Run Build Tool Plug-ins の項目を開き、+ボタンを押す。
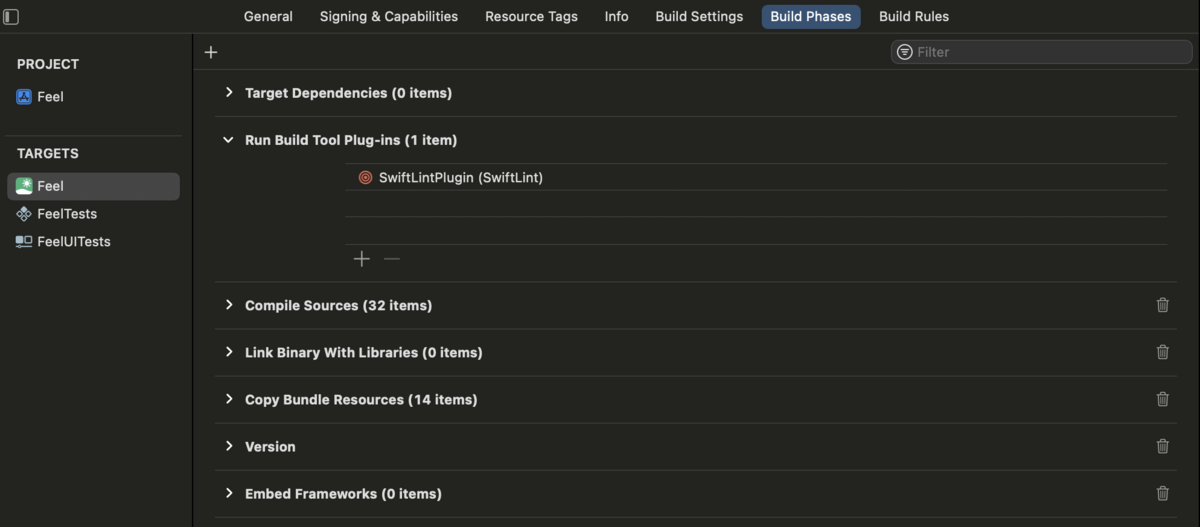
LicensePlistBuildTool を選び、Add する。
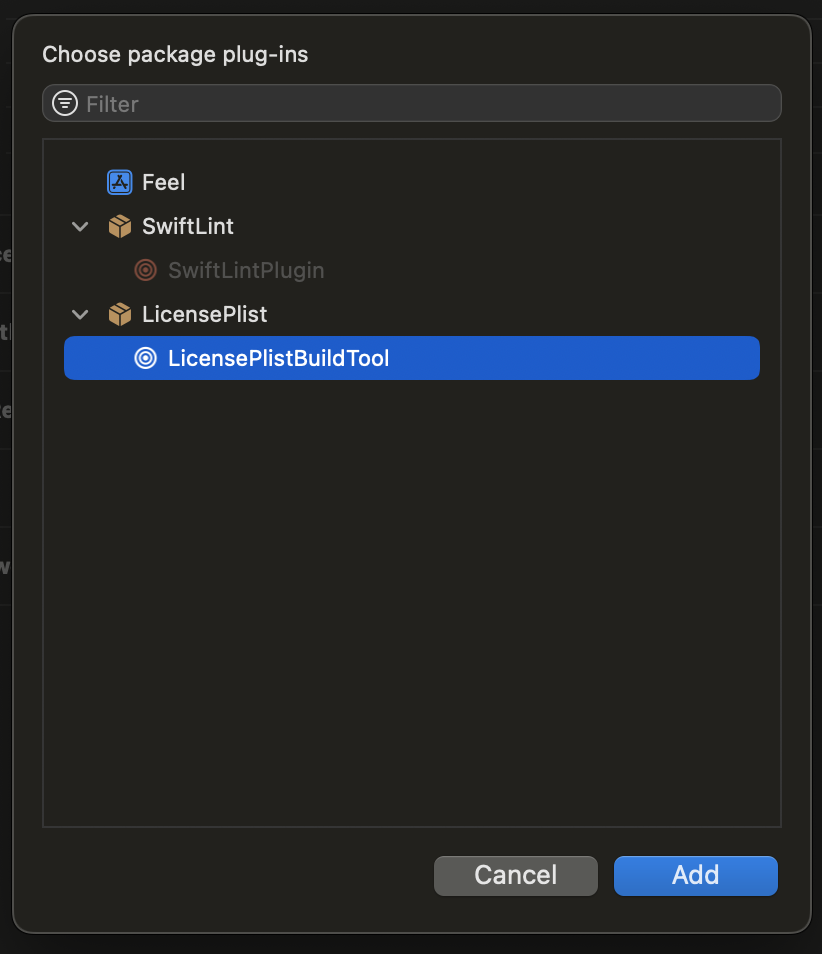
LicensePlistBuildTool が追加されたことが確認できる。
プロジェクトのルートフォルダに license_plist.yml を配置する。
最低限、以下の記述を追加する。
options: xcodeprojPath: "*.xcodeproj" # 対象のプロジェクトファイルのパス gitHubToken: ghp_XXX # GitHub トークン(LicensePlist は GitHub API を使うので、その制限エラーを避けるため)
Settings.bundle に LicensePlist の成果物をコピーする時には、公式ドキュメントにある以下のスクリプト(リンク)を BuildPhases に追加する。
echo "Will copy acknowledgements" ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS_DIR=${BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR}/${CONTENTS_FOLDER_PATH}/com.mono0926.LicensePlist.Output DESTINATION_PATH=${BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR}/${CONTENTS_FOLDER_PATH}/Settings.bundle/ cp -r "${ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS_DIR}"/* "${DESTINATION_PATH}" rm -rf "${ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS_DIR}"
私の環境では、プロジェクト内にある Settings.bundle に成果物をコピーしたかったので、DESTINATION_PATH を変えて以下のようにした。
echo "Will copy acknowledgements" ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS_DIR=${BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR}/${CONTENTS_FOLDER_PATH}/com.mono0926.LicensePlist.Output DESTINATION_PATH=${PRODUCT_NAME}/Settings.bundle/ cp -r "${ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS_DIR}"/* "${DESTINATION_PATH}" rm -rf "${ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS_DIR}"
Firebase
公式ドキュメントに Swift Package Manager の導入方法があるので、それに沿って導入できる。
パッケージ追加の画面で以下を検索して、Add Package する。
https://github.com/firebase/firebase-ios-sdk.git
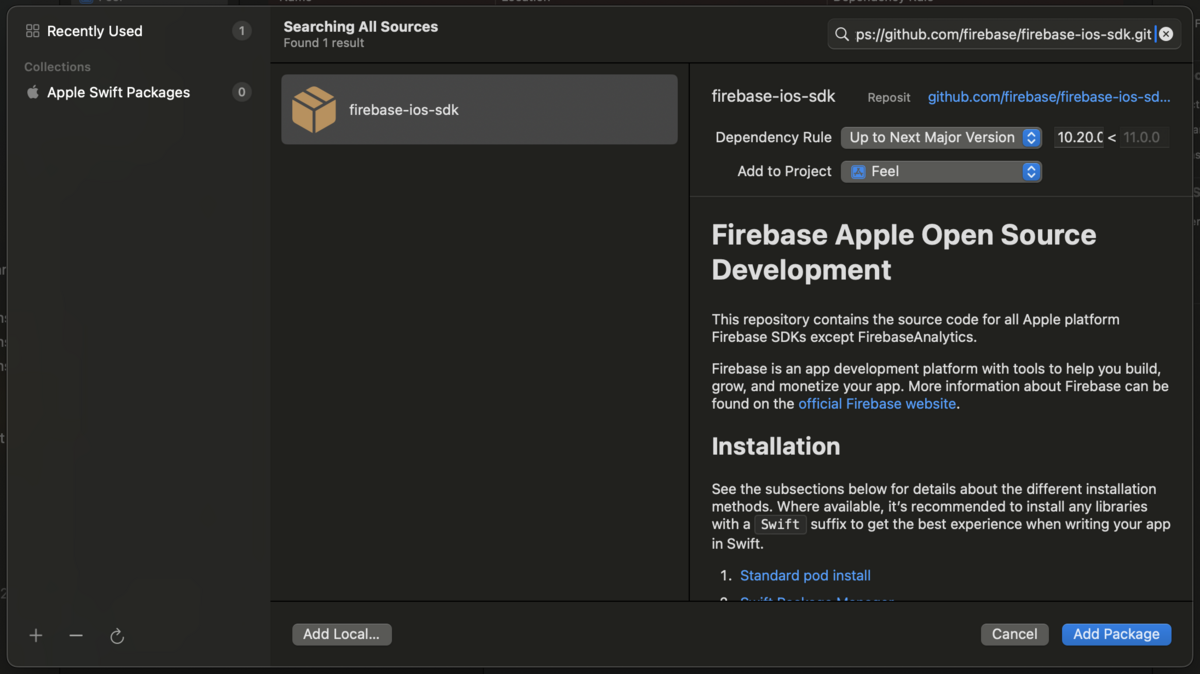
Package Product をターゲット追加する画面が表示されるので、使用するプロダクトを選んで、Add Package する。
今回は、Pods で AnalyticsWithoutAdIdSupport, Crashlytics を入れていたので、それらにターゲットを設定する。
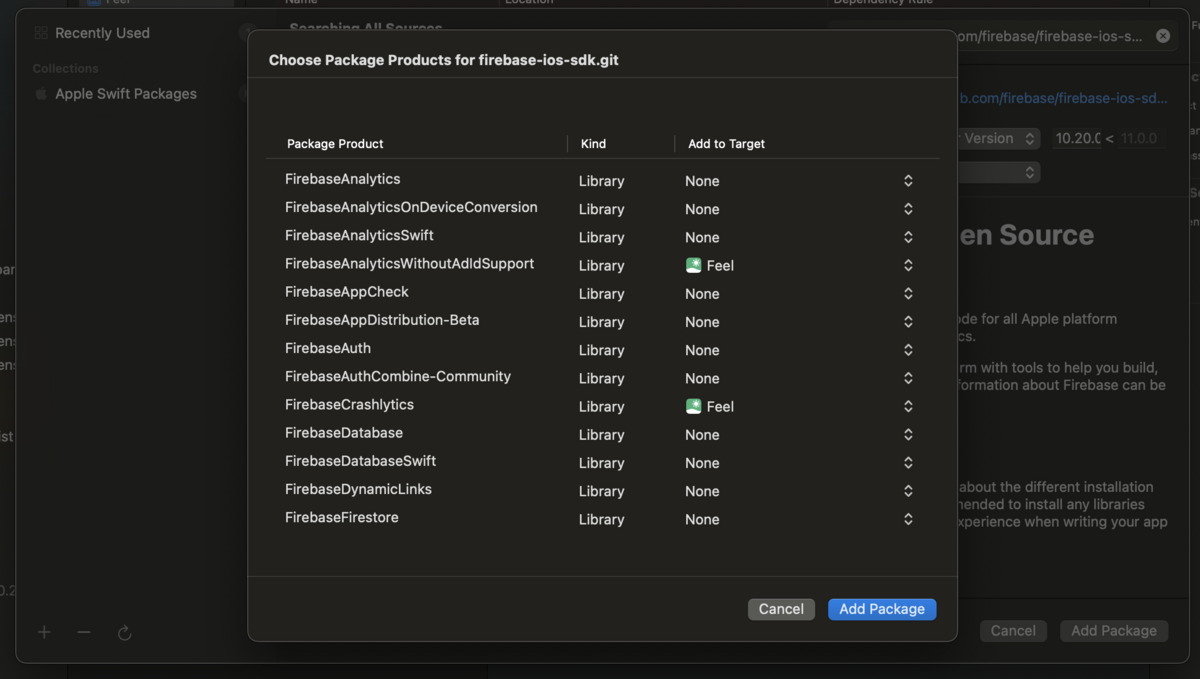
Xcode プロジェクトに Package が追加されたことが確認できる。

Crashlytics を使用する場合、ビルド後にデバッグシンボルをアップロードするシェル(リンク)を BuildPhases に追加する。
${BUILD_DIR%Build/*}/SourcePackages/checkouts/firebase-ios-sdk/Crashlytics/run
Firebase が正しく導入されたかをチェックするために、-FIRAnalyticsDebugEnabled を引数に追加してアプリを起動し、イベントを送信する。(最初のハイフンも含めることに注意)
Firebase Console の Debug View でイベントが確認できたら OK.
参考